Australia’s Disaster Ready Fund Backs AI for Bushfires and Heatwaves
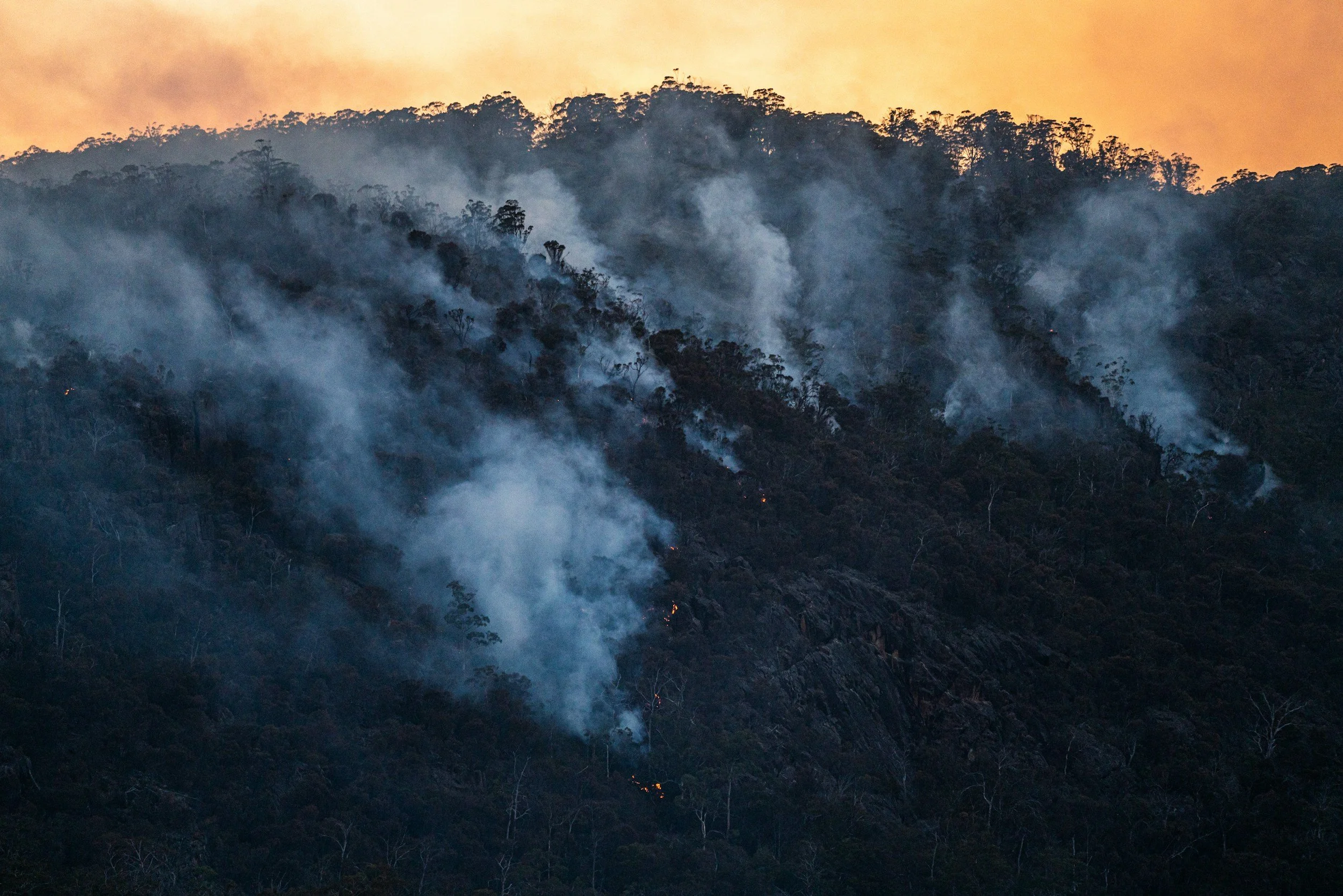
New project listings from the Disaster Ready Fund detail the integration of machine learning into Australian disaster response, specifically regarding bushfire detection in Victoria and heatwave surveillance in Western Australia. These initiatives mark a shift toward smart infrastructure and automated decision support in national emergency management.
AIMS Deploys AI and Robotics to Scale Coral Restoration
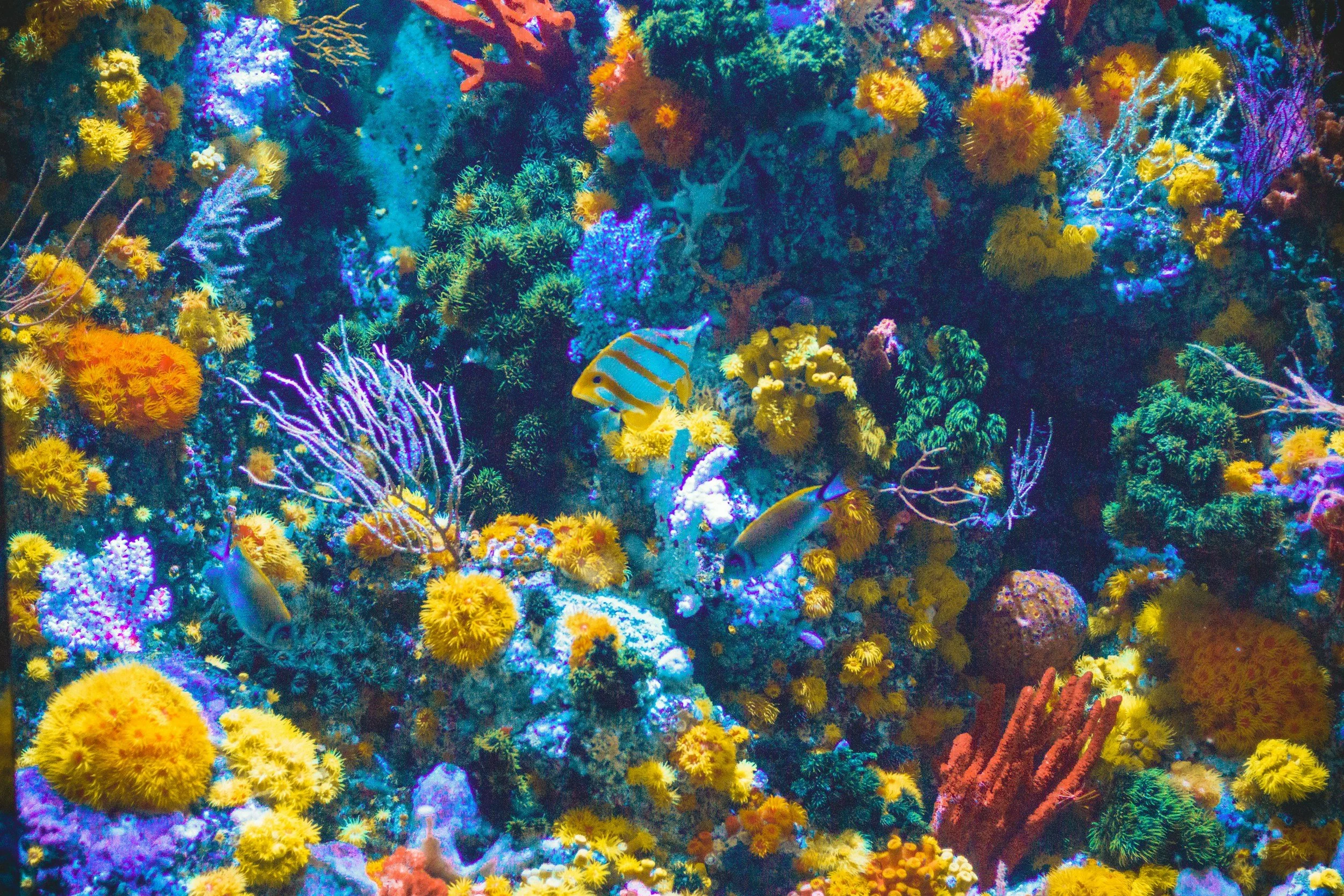
The Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS) is implementing AI-enabled automation to address production bottlenecks in coral aquaculture. The initiative includes systems for automated fertilization, computer vision for larval counting, and robotic deployment guidance to support restoration efforts on the Great Barrier Reef.
Prithvi CAFE: Hybrid AI Blends Tech to Improve Satellite Flood Mapping
A new preprint from researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and the University of Portsmouth introduces Prithvi CAFE, a hybrid AI architecture for flood inundation mapping. By combining the Prithvi EO 2.0 foundation model with a parallel CNN branch, the method aims to improve segmentation accuracy on unseen geographies while significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters required for fine-tuning.
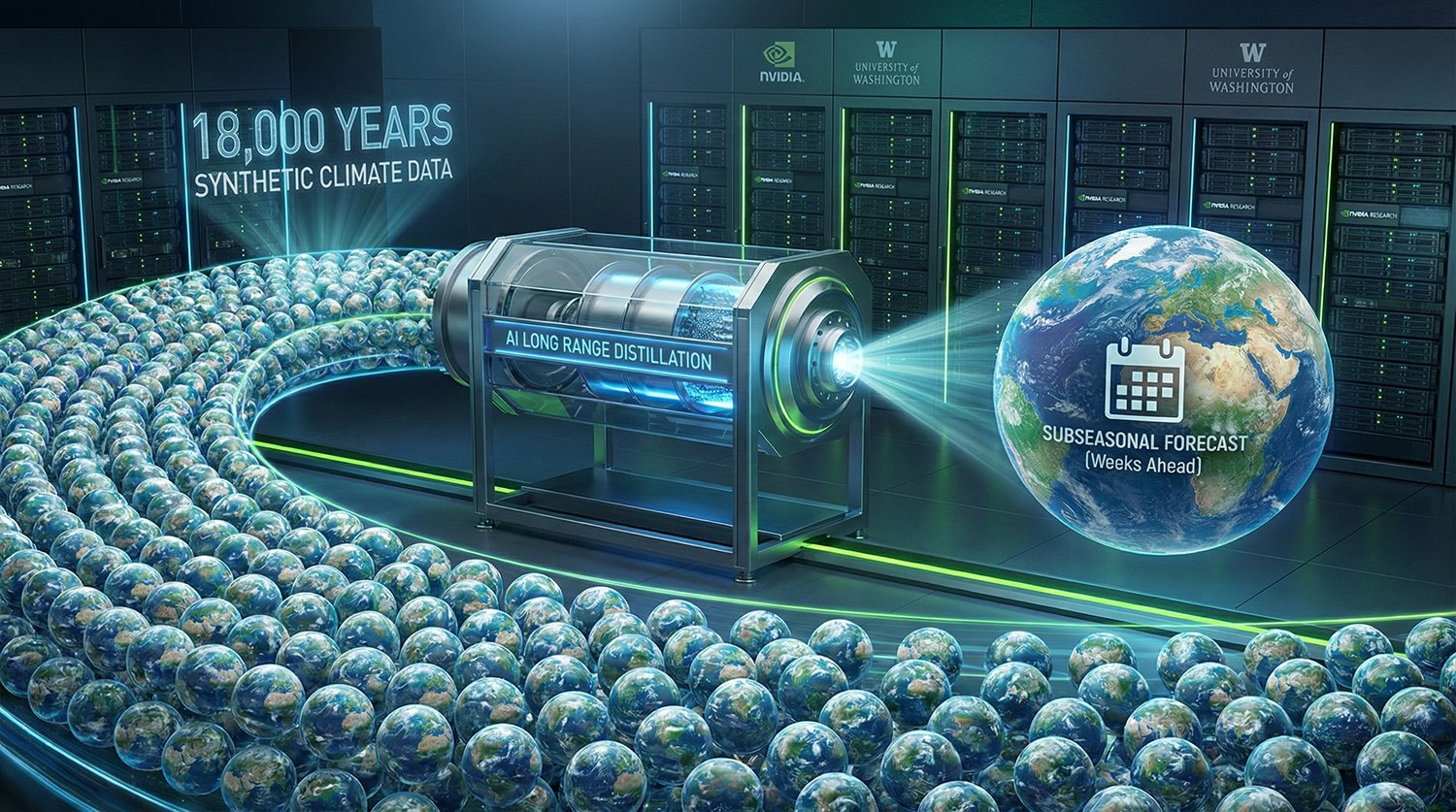
NVIDIA & UW Use 18,000 Years of Synthetic Climate for AI Forecasting
Researchers from NVIDIA and the University of Washington have introduced "long range distillation," a method that utilizes 18,000 years of synthetic climate data to train AI models for improved subseasonal to seasonal weather forecasting, addressing data scarcity in historical records.
Japan's B Alert System: AI-Powered Cameras Speed Up Bear Sighting Warnings
Japanese municipalities are adopting automated AI detection pipelines to manage a surge in bear sightings. The B Alert system uses cloud-based filtering to streamline camera data, enabling quicker notifications via disaster radio and email. This technology, alongside drone and 5G trials, represents a significant shift toward digital wildlife countermeasures.
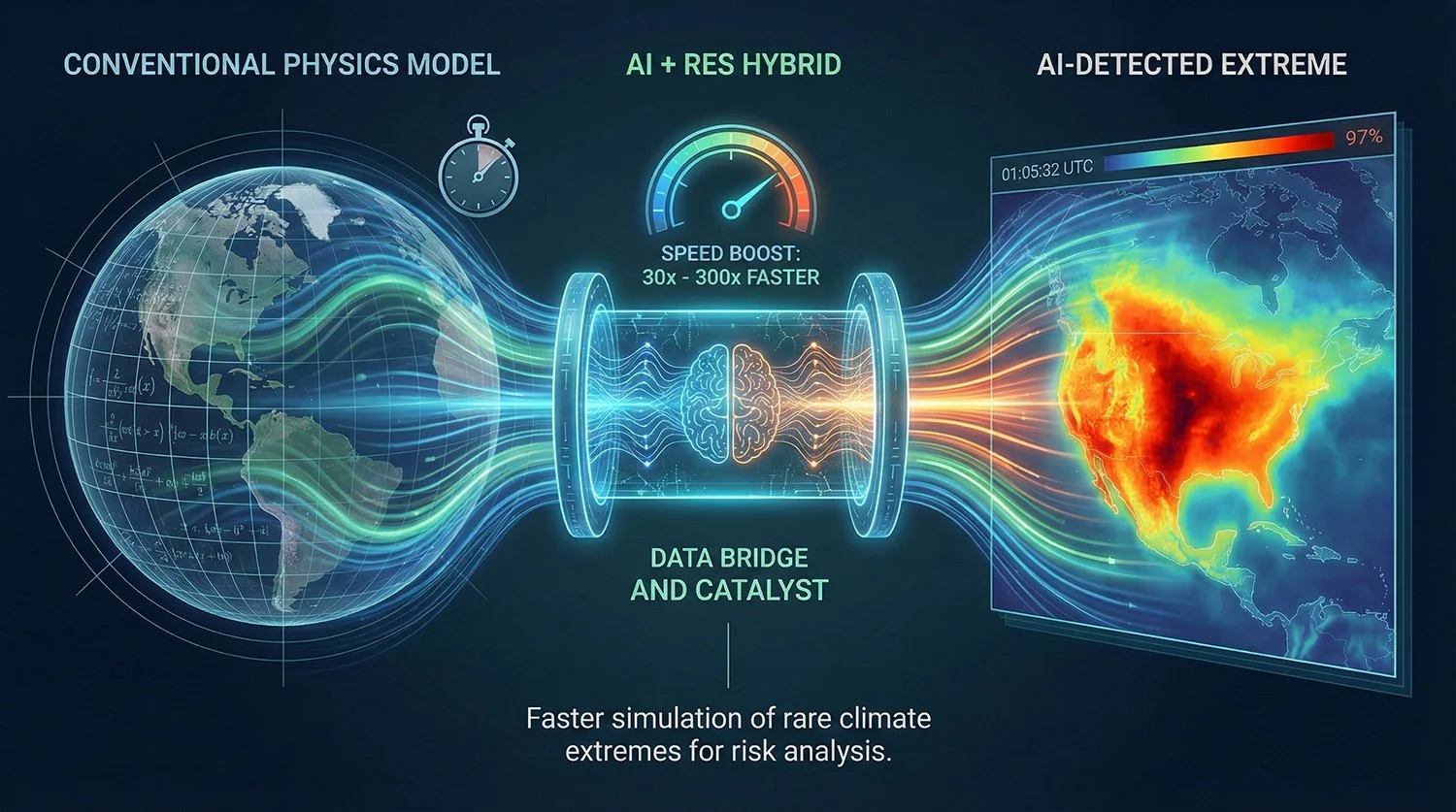
Hybrid AI Method Samples Rare Heatwaves 30-300x Faster Than Standard Models
A Nature News report details a new approach combining AI with physics-based climate models. The "AI plus RES" method estimates rare extreme heat events 30 to 300 times faster than conventional simulations, aiming to improve climate risk analysis.
New Artificial Neurons Mimic Biology with 60mV Signals to Cut AI Power
Researchers have published two separate studies detailing artificial neurons that utilize ion motion to closely mimic biological signal processing. By operating at low voltages around 60 millivolts and integrating with chemical sensors, these components aim to reduce the power and circuit overhead required for running artificial intelligence on edge devices.
AI Robot Guides Great Barrier Reef Coral Seeding with 77.8% Accuracy
The Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS) has begun field trials of the Deployment Guidance System (DGS), an AI-enabled workflow that automates the placement of juvenile corals. Designed to scale restoration efforts, the system uses real-time computer vision to select optimal seeding sites across the Great Barrier Reef, responding to the urgency of back-to-back mass bleaching events in 2024 and 2025.
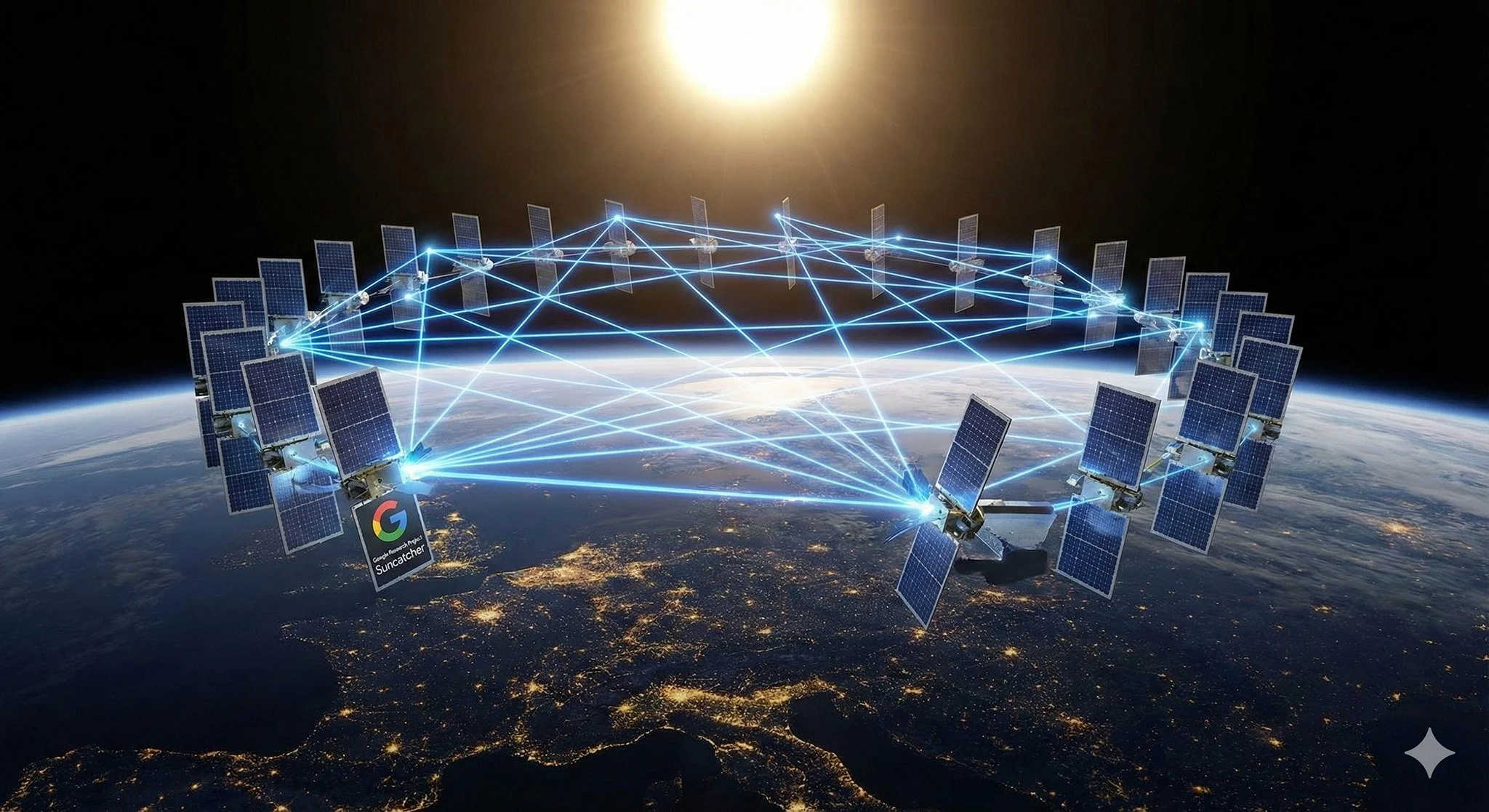
Google Explores Space-Based AI with 81-Satellite Solar Clusters
In a new technical paper, Google outlines Project Suncatcher, a research initiative designed to test whether artificial intelligence workloads can be offloaded to solar-powered satellites. The proposal describes formation-flying clusters capable of high-speed optical data transmission to address power grid constraints on Earth.
New AI Tool Cuts Data Center CO2 by 45% and Extends Server Life by 1.6 Years
A new study from the University of California, Riverside introduces "Federated Carbon Intelligence," a software framework designed to optimize AI data centers. By balancing real-time hardware health with local power grid data, the system aims to reduce carbon emissions significantly while extending the operational life of server fleets.
Stanford AI Designs 16 Functional Viruses from 302 Synthetic Genomes
In a September 2025 study, scientists from Stanford University and the Arc Institute demonstrated that artificial intelligence can design fully functional viral genomes. Using the Evo 2 large genome model, the team synthesized 302 unique DNA sequences, resulting in 16 viable bacteriophages capable of infecting and lysing E. coli bacteria.
AI Report Reveals How 20M Sq Ft of Smart Buildings Are Moving Toward 2030 Autonomy
Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping commercial buildings by improving energy efficiency, refining space usage, and responding to fluctuating occupancy patterns. Drawing on 20 million square feet of global sensor data, a new Tradeline analysis outlines how predictive HVAC control, air-quality monitoring, and dynamic restacking are preparing organisations for a future where early autonomous buildings could appear as soon as 2030.
Google Expands Earth AI Access, Deploying 3-Model Geospatial Reasoning Agent After Oct 23 Rollout
Google has expanded access to its AI-driven Geospatial Reasoning agent, allowing authorised users to query satellite imagery and environmental data in plain English. The tool is powered by Gemini and currently remains in a staged rollout, with wider release planned.
MIT Researchers Develop Ionic Neuromorphic Chips to Cut AI Energy Use by Up to 1,000×
Researchers at MIT are exploring neuromorphic computing designs that replicate how the human brain processes information, aiming to lower the energy demands of modern AI. Their ionic synapse devices store and compute data in one place, reducing the costly data shuttling that occurs in traditional chips. The work could enable more efficient AI in wearables, sensors, and other low-power environments.
Origin Bio’s Axis AI Model Outperforms AlphaGenome by 6.7% in Regulatory DNA Prediction
Origin Bio has launched Axis, an AI model developed to design and analyze regulatory DNA sequences for gene and cell therapy research. The model integrates sequence generation and functional prediction in a single framework and has been benchmarked against existing genomic models. Researchers can request API access while laboratory validation progresses.
TuNaAI Boosts Nanoparticle Drug Delivery: 42.9% Higher Success and 75% Safer Formulation
TuNaAI represents a shift toward data-guided formulation in nanomedicine. By analysing real-world formulation outcomes, the platform predicts optimal combinations of drugs and excipients, improving reliability and reducing associated risks in therapeutic development.
Google DeepMind Releases Perch 2.0 to Identify Wildlife from 1.5M+ Audio Recordings
Google DeepMind has released Perch 2.0, an enhanced open-source audio-recognition model that broadens species coverage to mammals, amphibians and insects beyond birds. With training on over 1.5 million recordings and a streamlined architecture, the tool enables conservationists to analyse vast soundscapes faster, supporting efforts to monitor ecosystems from forests to reefs.
USC AI Model Simulates 4 Billion Atoms to Advance Carbon-Neutral Concrete Design
A team at USC’s Viterbi School of Engineering has introduced Allegro-FM, an AI model that simulates billions of atoms with quantum-level accuracy. By modeling how concrete can reincorporate CO₂ during production, the research points toward more sustainable construction methods and faster material innovation.
USC Engineers Develop AI Model for Subsurface Fluid and Heat Flow Predictions
The University of Southern California’s Viterbi School of Engineering is leading a project called PINCER, a physics-informed causal deep learning model designed to improve predictions of fluid, CO₂, and heat movement in underground formations. Backed by NSF funding, the work supports applications in carbon storage, geothermal energy, and groundwater management, while addressing challenges in modeling subsurface systems.
AI Breakthrough Boosts Self-Driving Labs, Speeds Materials Discovery by Ten Times
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed an AI-powered dynamic flow method that enables self-driving laboratories to generate up to 10 times more data than earlier approaches. The system reduces chemical consumption, accelerates experimentation, and enhances sustainability, potentially shortening materials discovery cycles from years to days.