AI-Environmental Journalism Model Enhances Real-Time Hazard Detection and Reporting
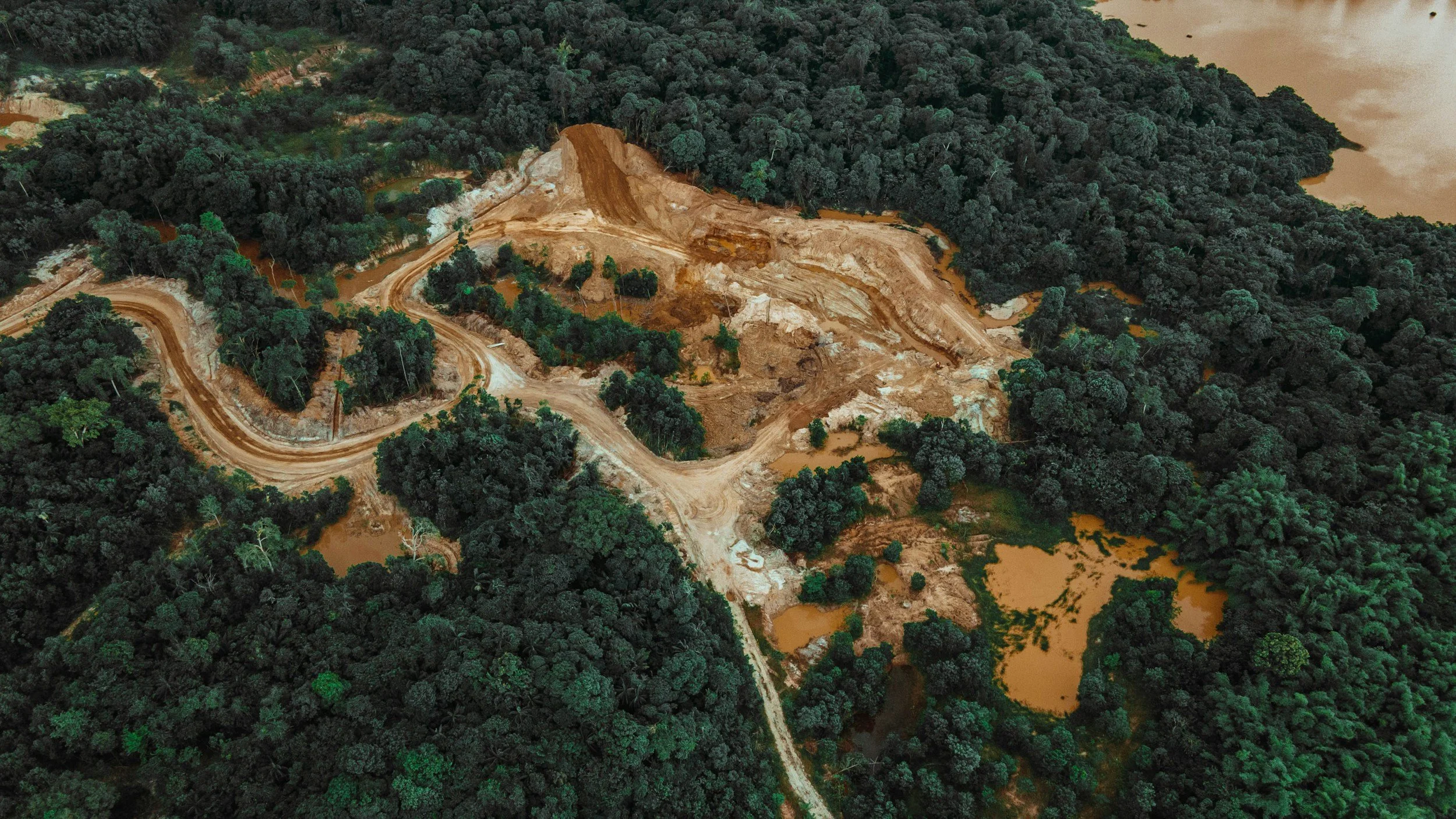

Image Credit: Renaldo Matamoro | Splash
The AI-Environmental Journalism Integration Model (AEJIM) is a new framework designed to improve the detection and reporting of environmental hazards in real time. By integrating artificial intelligence data analysis with community input, AEJIM seeks to deliver faster and more accurate environmental news. It focuses on addressing monitoring gaps, particularly in regions with limited resources, and aims to support global decision-making.
[Read More: The Future of Earth System Science: Embracing AI for a Sustainable Planet]
How AEJIM Uses AI for Detection
AEJIM employs AI to process large datasets, enabling rapid identification of environmental hazards such as pollution or deforestation. Machine learning, a key AI technique, detects patterns that might be overlooked by traditional methods, like changes in air quality. While specific data sources for AEJIM are not detailed, AI environmental tools typically analyze information from satellites, sensors, and weather stations to provide real-time insights. This speed is vital for timely reporting, especially in areas prone to environmental risks.
[Read More: AI Tools Shape Efforts to Combat Air Pollution, Raise Energy Concerns]
Crowdsourced Validation for Accuracy
To ensure reliability, AEJIM incorporates crowdsourced validation, where local communities provide on-the-ground observations to verify AI findings. This approach helps correct potential AI errors and enhances trust in the system. It also empowers residents in under-monitored regions to contribute to global environmental awareness by reporting issues like water contamination or illegal logging. Combining local knowledge with technology improves the accuracy of hazard detection, making AEJIM a collaborative model.
[Read More: AI Technology Aids Ocean Microplastic Research]
Supporting Global Decision-Making
AEJIM’s real-time data is designed to inform policymakers and organizations worldwide. Accurate environmental information is crucial for developing effective policies, as emphasized by the United Nations Environment Programme. By providing reliable reports, AEJIM could influence decisions on climate change or disaster response. Its use of transparent AI methods, such as Explainable AI, aligns with calls for open processes in journalism to build public trust.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
AEJIM faces challenges, including the risk of AI generating inaccurate results, known as “hallucinations”. Ethical concerns, such as ensuring fairness and transparency in AI journalism, are significant, as noted in recent studies. AEJIM’s crowdsourced validation and transparent AI methods aim to address these issues, but scaling the model globally will require careful oversight to avoid biases or unequal access to technology.
[Read More: Top 10 AI Terms of 2024: Key Innovations Shaping Artificial Intelligence]
Source: arXiv, Science Direct, Frontiers, UN Environment Programme, Springer Nature
We are a leading AI-focused digital news platform, combining AI-generated reporting with human editorial oversight. By aggregating and synthesizing the latest developments in AI — spanning innovation, technology, ethics, policy and business — we deliver timely, accurate and thought-provoking content.