Morse Micro Ships HaLowLink 2: Long-Range Wi-Fi HaLow Gateway for IoT

Image Source: Morse Micro
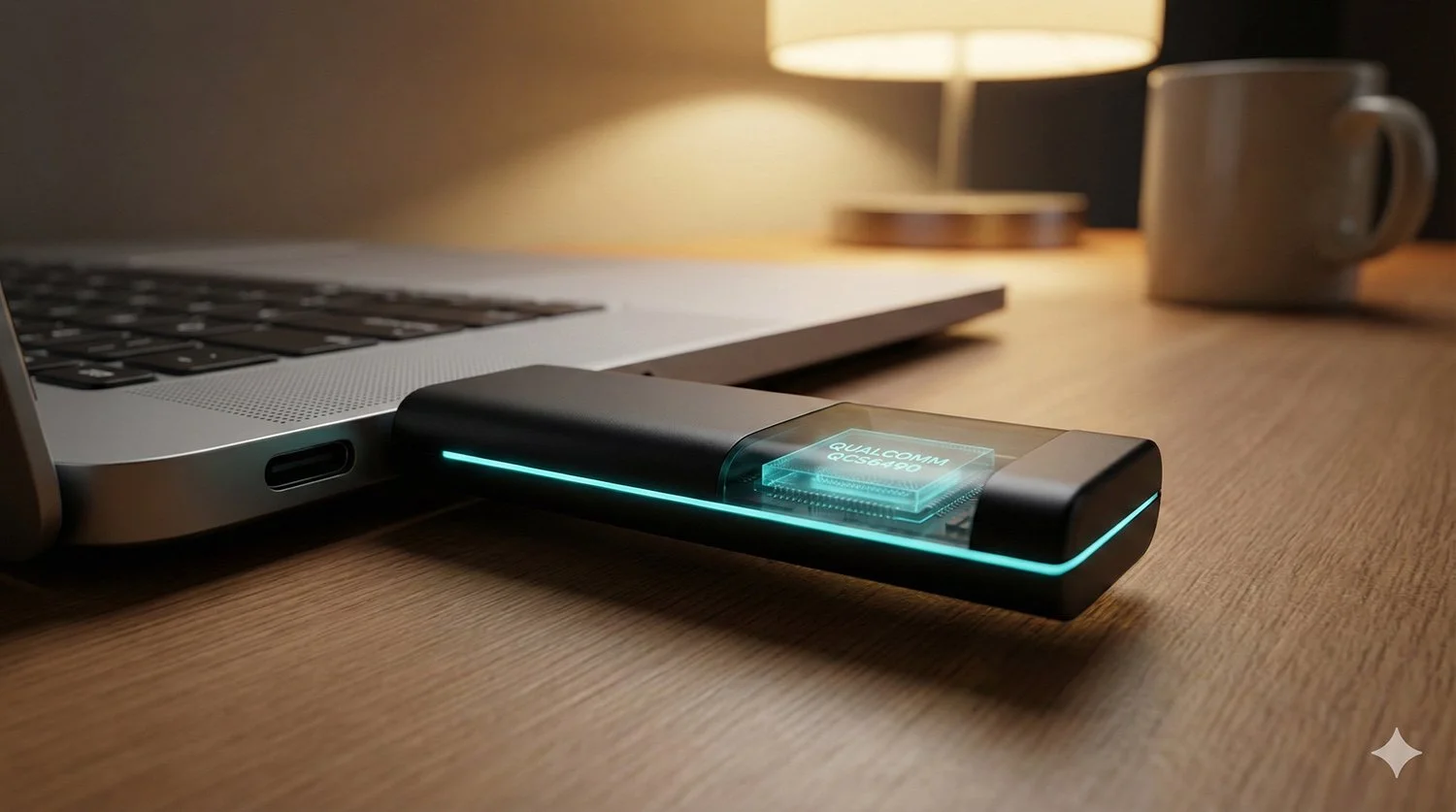
Sydney based Morse Micro has announced general availability for HaLowLink 2, a Wi Fi HaLow platform that combines router, access point and extender roles and is being positioned as a faster way for developers and integrators to roll out long range, low power wireless networks for IoT style deployments.
Shipping Globally
The general availability announcement was published during CES 2026 and describes HaLowLink 2 as now shipping globally, with sales routed via distribution.
In parallel, Morse Micro product materials describe HaLowLink 2 as a next generation gateway designed for multiple regions, including Australia, with a hardware and software stack built around the company’s MM8108 Wi Fi HaLow chipset.
Better Penetration
Wi Fi HaLow is based on IEEE 802.11ah and operates in sub 1 GHz spectrum, which generally trades peak speed for better reach and better penetration through obstacles compared with conventional Wi Fi bands. Wi Fi Alliance materials highlight that many IoT environments need longer range links, the ability to pass through multiple walls, and devices that can run for months or years on a battery, which is the niche HaLow targets.
HaLowLink 2 is presented as an all in one gateway that can be deployed as:
a HaLow router
a HaLow access point
a HaLow extender
It also includes a 2.4 GHz Wi Fi radio, intended for local connectivity alongside the HaLow link, and Morse Micro notes a paired setup can push 2.4 GHz hotspots beyond the reach of a single conventional access point by using HaLow as the long range link between nodes.
From the published product brief, key implementation details include:
802.11ah channel bandwidth support listed as 1, 2, 4 and 8 MHz
CPU listed as MediaTek MT7621, with 256 MB DRAM and 32 MB NAND flash
radios listed as Morse Micro MM8108 for 802.11ah and MediaTek MT7603E for 802.11n
interfaces listed as two gigabit Ethernet ports plus one USB C port that carries power and Ethernet data
software listed as OpenWrt 23.05 with a web UI plus SSH and CLI configuration, and streamlined upgrades via an online server
physical and environmental specs including 88 x 68 x 24 mm, and an operating range listed as 0 to 40 C
One practical point is that transmit power limits vary by region. The product brief notes EU and UK transmit power limited to 14 dBm and Japan limited to 16 dBm, while also listing “up to 26 dBm” in the general technical specs section. In other words, real world range will depend heavily on the local regulatory domain and configuration.
Benefits of a Longer Wi-Fi Range with the Adoption of Edge AI
Most real world AI systems begin with data collection, including sensors, meters, cameras, machinery telemetry, and environmental monitoring. In practice, the primary bottleneck is often not model accuracy but coverage and uptime. This determines how many devices can be deployed, how far they can operate from network infrastructure, and how frequently they require maintenance.
As adoption of edge AI increases, more devices are performing lightweight inference locally and transmitting only events, summaries, or compressed features upstream. In these scenarios, longer range and lower power wireless links can significantly expand the footprint of sensor networks. This is particularly relevant for large environments such as agriculture, logistics yards, utilities, and smart city corridors, where installing new cabling or dense Wi Fi infrastructure can be complex and costly.
The Wi Fi Alliance positions Wi Fi HaLow as an IoT focused extension of Wi Fi, combining sub 1 GHz operation with native IP networking and security expectations aligned with mainstream Wi Fi. This framing helps explain why vendors are presenting HaLow as a more accessible entry point for IoT deployments compared with some specialised low power networking stacks.
Compatibility
HaLowLink 2 vs HaLowLink 1: HaLowLink 1 is earlier generation, listed as using the MM6108 chipset and supporting fewer regions. Wi Fi Alliance certification records show HaLowLink 1 certified under Wi Fi CERTIFIED HaLow, which is a useful benchmark for interoperability expectations. HaLowLink 2 expands the stated regional support set and moves to MM8108, but a comparable public Wi Fi Alliance certificate was not identified in the sources reviewed here, so any certification status should be treated as unconfirmed unless Morse Micro or the Alliance publishes it.
All in one gateway vs embedded modules: For product builders who want HaLow inside their own hardware rather than as an external gateway, a parallel track is HaLow modules and M.2 cards. For example, Gateworks announced an M.2 Wi Fi HaLow card based on MM8108 aimed at industrial IoT and edge computing integrations, which is the “build it in” approach compared with HaLowLink 2’s “deploy it fast” approach.
We are a leading AI-focused digital news platform, combining AI-generated reporting with human editorial oversight. By aggregating and synthesizing the latest developments in AI — spanning innovation, technology, ethics, policy and business — we deliver timely, accurate and thought-provoking content.