Applied Materials (AMAT) Stock Forecast: Comparing Six AI Chatbot Price Predictions

Disclaimer: This article is for informational and educational purposes only. The predictions and analyses presented herein were generated by AI systems and should not be construed as financial advice, investment recommendations, or solicitations to buy or sell any securities. Stock prices are inherently unpredictable, and all investments carry risk of loss. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Readers should consult qualified financial advisors before making any investment decisions. TheDayAfterAI News and its contributors do not accept liability for any losses arising from reliance on this content.
At TheDayAfterAI News, we are pioneering a unique approach to financial analysis: harnessing the collective intelligence of today’s leading AI chatbots to generate short-term stock price forecasts. In this instalment of our ongoing series, we tasked six of the most widely used AI chatbots — ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Grok, Perplexity, and Copilot — with the same challenge: predict the price trajectory of Applied Materials (NASDAQ: AMAT) over the five trading sessions from Friday, February 13 to Friday, February 20, 2026.
Each chatbot was given identical prompts and access to the same publicly available market data. They were asked to provide a predicted opening price (Feb 13), a predicted closing price (Feb 20), a probability assessment of whether the stock would rise or fall over the period, an estimated price range, and a session-by-session forecast path. The results reveal both a striking degree of consensus and notable divergences in methodology and confidence levels.
Why AMAT, and Why This Week?
Applied Materials is a bellwether of the semiconductor equipment industry and a direct beneficiary of the global AI infrastructure buildout. The forecast window was chosen deliberately because it presented an unusually dense confluence of market-moving events:
Earnings Catalyst: AMAT reported a blowout Q1 FY2026 after the close on February 12, beating consensus on both EPS ($2.38 vs. $2.19–$2.21 expected) and revenue ($7.01B vs. $6.88B expected), while guiding Q2 revenue to $7.65B — a staggering 9% above Street estimates.
Macro Data: January CPI released on the morning of February 13 came in at 2.4% YoY, below the 2.5% consensus, providing a disinflationary tailwind for growth stocks.
Regulatory Resolution: AMAT settled its $252.5M export-control penalties with the Bureau of Industry and Security on February 11, removing a persistent regulatory overhang.
Structural Events: The week included a US market holiday (Presidents’ Day, Feb 16), monthly options expiration (Feb 20), VIX futures expiry (Feb 18), FOMC minutes (Feb 18), and AMAT’s ex-dividend date (Feb 19).
This “perfect storm” of catalysts made AMAT an ideal test case for evaluating how different AI models weigh fundamental, technical, macro, and structural factors in short-term forecasting.
Headline Predictions at a Glance
The table below summarises the core predictions from each chatbot. All six were bullish, but the degree of conviction and the specific price targets varied meaningfully.
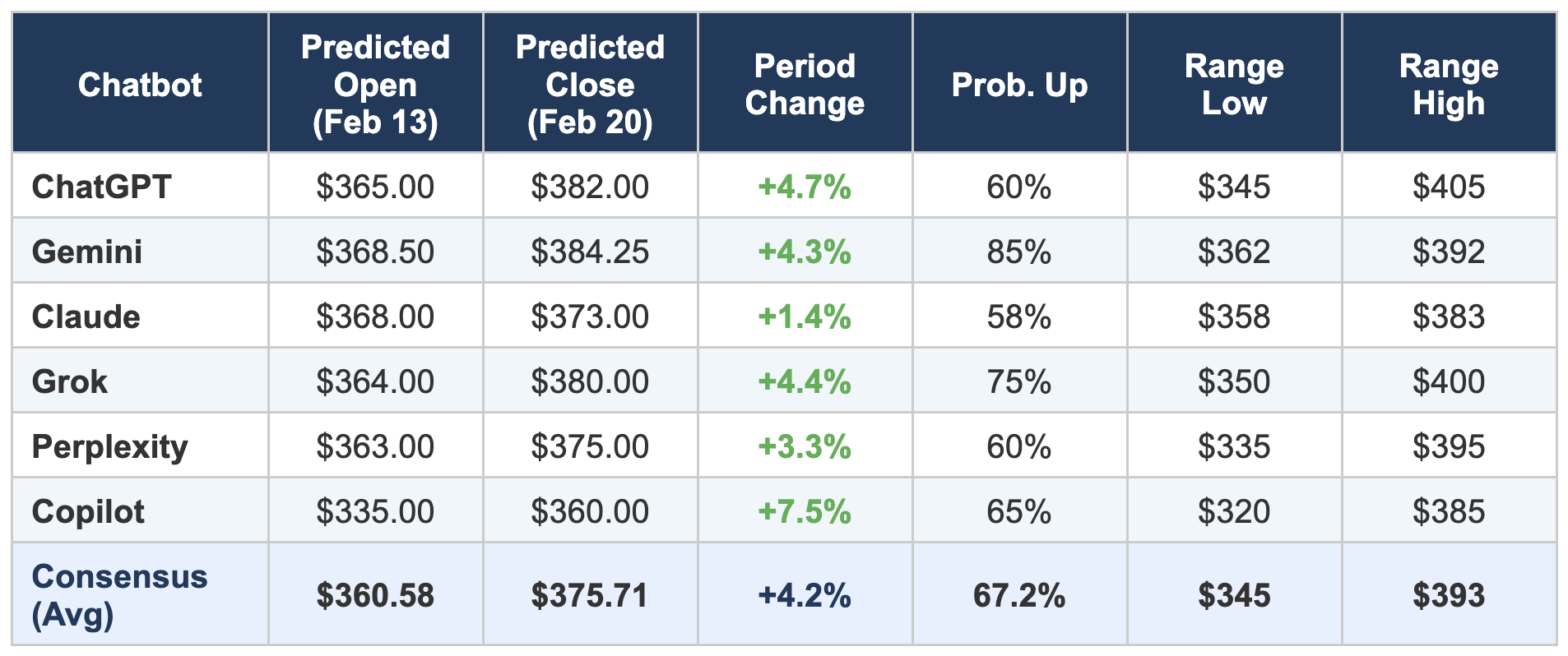
Note: Consensus figures are simple averages across all six chatbots. Copilot’s opening price estimate appears to have been based on the pre-earnings closing price rather than the post-earnings pre-market level, which accounts for its significant deviation from the other five models.
Key Observations
1. Universal Bullish Consensus
All six chatbots predicted AMAT would finish the week higher than its opening price on February 13. The probability assessments ranged from a cautious 58% (Claude) to an assertive 85% (Gemini). This unanimity reflects the overwhelming weight of the earnings catalyst: a beat-and-raise quarter driven by AI-related semiconductor demand is precisely the kind of fundamental event that all models, regardless of methodology, interpret as directionally positive.
2. The Opening Price Divergence
Five of the six chatbots converged on an opening price in the $363–$369 range, consistent with pre-market trading levels observed on the morning of February 13 after the post-earnings after-hours surge. The outlier was Copilot at $335, which appears to have anchored its opening estimate closer to the February 12 closing price of $328.39 rather than accounting for the overnight repricing. This is a notable methodological gap — the model seemingly did not fully incorporate the after-hours and pre-market price action into its starting reference point.
3. Closing Price Spread: Cautious vs. Euphoric
The predicted closing prices on February 20 ranged from $360 (Copilot) to $384.25 (Gemini), a spread of $24.25. Excluding Copilot’s lower baseline, the remaining five models clustered between $373 and $384, suggesting a consensus end-of-week target in the mid-$370s to low-$380s. Claude was the most conservative among the five pre-market-aware models, projecting just a +1.4% gain, explicitly citing AMAT’s historical pattern of post-earnings sell-offs and OPEX headwinds. Gemini was the most bullish, projecting +4.3% with 85% confidence, heavily weighting the gamma squeeze thesis and dealer hedging dynamics.
4. Volatility Expectations
The estimated price ranges reveal differing assumptions about volatility. Perplexity projected the widest range ($335–$395, a $60 spread), reflecting its emphasis on the elevated VIX environment and the possibility of sharp intraday reversals. Gemini projected the narrowest range ($362–$392, a $30 spread), consistent with its high-conviction bullish thesis that the gamma squeeze dynamics would limit downside. ChatGPT’s range ($345–$405) was the most aggressive on the upside, being the only model to contemplate prices above $400 during the week.
5. Where the Models Agreed Most
Despite their differences, all six models converged on several key themes. The earnings beat and forward guidance were universally identified as the primary bullish catalyst. All models recognised the January CPI print as a supportive macro tailwind. The prior 52-week high of $344.60 was consistently identified as the critical support level that must hold for the bullish thesis to remain intact. And all models flagged FOMC minutes on February 18 and monthly options expiration on February 20 as the week’s most significant risk events.
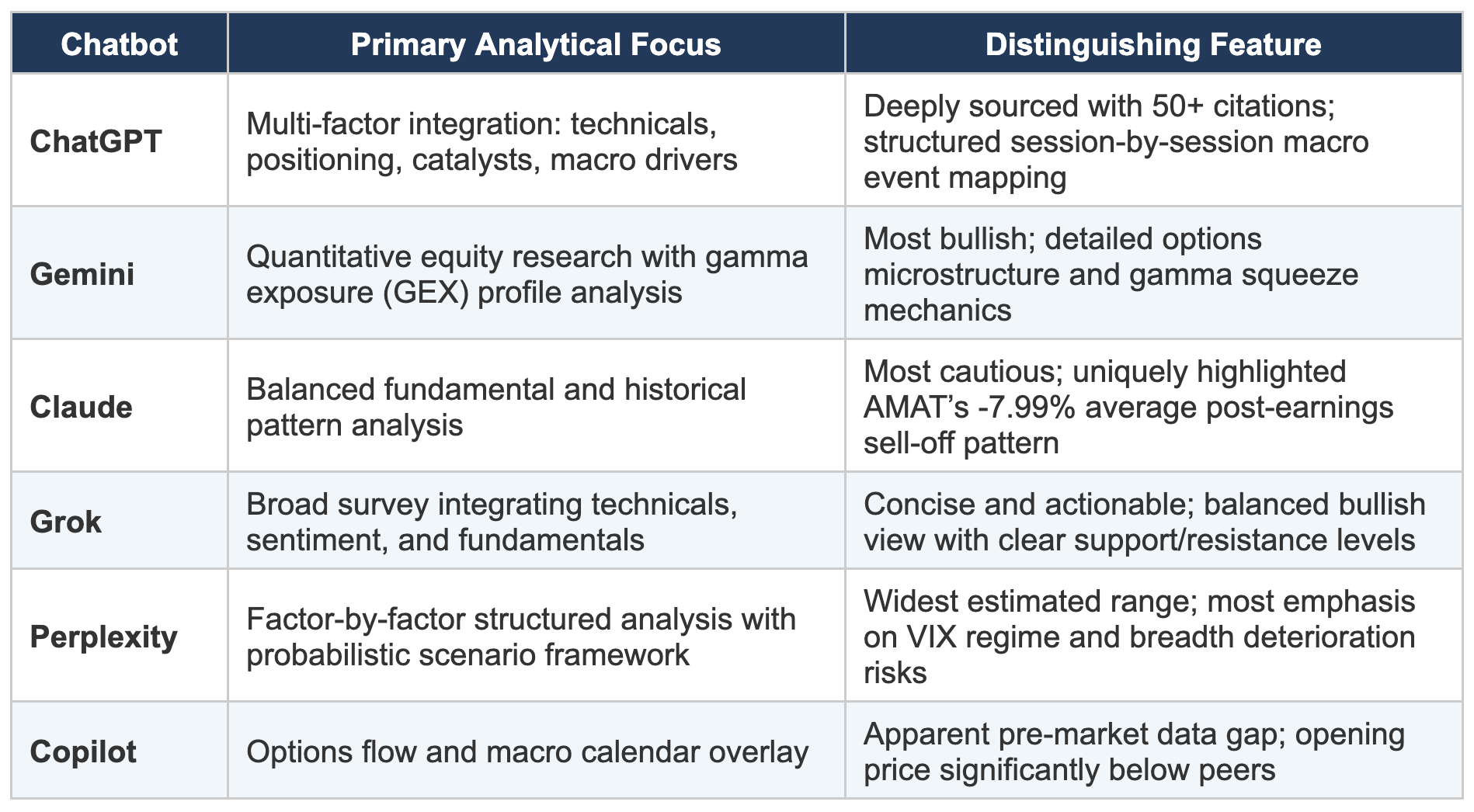
How Each Chatbot Approached the Forecast
While all six chatbots drew from similar data sources, their analytical frameworks and emphasis areas differed in revealing ways:
Critical Levels and Events to Watch
Synthesising across all six analyses, the following levels and events emerged as consensus focal points for the week:
Key Price Levels
Critical Support — $344–$345: The prior 52-week/all-time high. All models agree that a close below this level would invalidate the breakout thesis.
Near-Term Support — $358–$365: The post-earnings gap zone. Holding this range on any pullback would confirm buyer conviction.
Upside Resistance — $380–$385: Psychological round number and options strike concentration. Multiple models project the week ending near this zone.
Stretch Target — $400+: Only achievable in the bull scenario. ChatGPT and Grok’s range highs contemplate this level.
Key Events
Tuesday Feb 17 — Retail Sales: The first major macro data point after the long weekend. Strong data could push yields higher and pressure growth multiples.
Wednesday Feb 18 — FOMC Minutes: The single most frequently cited risk event. While the minutes reflect pre-CPI sentiment, any hawkish surprise could trigger algorithmic selling.
Thursday Feb 19 — Ex-Dividend ($0.46): A small mechanical price adjustment, but noteworthy in a volatile environment.
Friday Feb 20 — Monthly Options Expiration: The structural event that all models identified as capable of amplifying whatever directional trend has established itself by week’s end.
Our Editorial Take
The exercise of comparing six AI chatbots on the same forecasting task yields insights that go beyond any single prediction. Several themes stand out.
Data quality is paramount. Copilot’s significantly lower opening price estimate demonstrates that even sophisticated models can produce materially different outputs when they anchor on stale data. The ability to incorporate real-time pre-market pricing was a clear differentiator among the models.
Analytical depth varies widely. ChatGPT’s 50+ citation, multi-factor framework and Gemini’s quantitative gamma exposure analysis contrast sharply with Copilot’s more concise approach. For readers seeking to understand the “why” behind a forecast, the depth of reasoning matters as much as the price target itself.
Contrarian signals have value. Claude’s uniquely cautious stance — explicitly citing AMAT’s -7.99% average post-earnings day move and the sell-the-news pattern — serves as an important counterweight to the bullish consensus. In markets, the most valuable analysis is often the one that challenges prevailing sentiment.
Consensus is not certainty. Even with all six models agreeing on the direction, the probability assessments averaged just 67%. The AI models themselves are telling us there is roughly a one-in-three chance the stock finishes the week lower. This is a healthy reminder that forecasting, even by advanced AI, remains fundamentally probabilistic.
Conclusion
The AI consensus for AMAT’s February 13–20 trading window is constructive: a predicted opening around $361–$369 (excluding the Copilot outlier), a closing target in the $373–$384 range, and a roughly two-thirds probability of finishing the week in positive territory. The fundamental catalyst — a transformative earnings report powered by AI-driven semiconductor demand — is strong, but the tactical environment (elevated VIX, dense macro calendar, OPEX mechanics) introduces meaningful two-way risk.
A new report by the University of Canberra and DroneShield identifies no recorded domestic drone-enabled cyber incidents in Australia to date, though researchers warn that limited detection capabilities may be obscuring the true threat landscape. This analysis examines the report's findings on critical infrastructure vulnerabilities, the role of AI in drone operations, and the Australian Government's recent regulatory updates regarding counter-drone enforcement and safety.
On January 16, 2026, the UK government expanded the Regulatory Innovation Office's (RIO) remit to prioritize robotics and defence technologies. The announcement includes a new "Front Door" pilot designed to identify and reduce cross-regulator barriers that delay the deployment of autonomous systems, such as inspection drones. This initiative seeks to coordinate approvals across aviation, data protection, and sector-specific safety authorities to streamline the path to market for AI-enabled technologies.
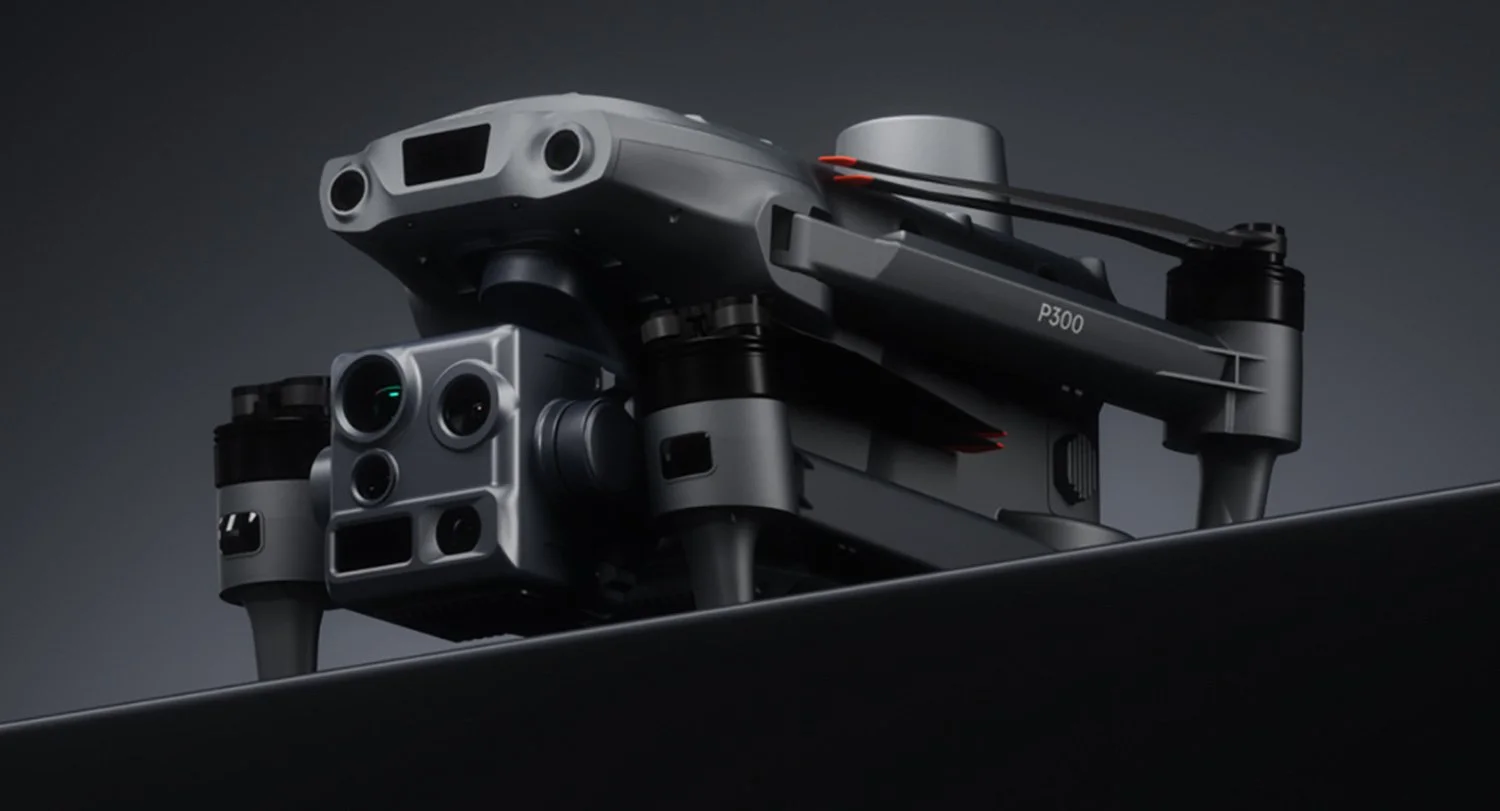
GDU has introduced the UAV P300 at CES 2026, an enterprise drone targeting the public safety and infrastructure sectors. This report details the manufacturer's claims regarding AI-enhanced visibility in adverse weather, obstacle avoidance technology, and autonomous navigation. It also examines how the P300 compares to competitor models from DJI and Skydio, while noting relevant regulatory factors that may impact availability.
Israel’s Ministry of Defence officially handed over the first operational Iron Beam system to the IDF in late December 2025. Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, the high-power laser is designed to neutralize aerial threats such as drones and mortars using thermal sensors and real-time computing. It will operate alongside the Iron Dome as a cost-effective, software-driven defense layer, with serial production now underway.
On 22 December 2025, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) expanded its "Covered List" to include foreign-made uncrewed aircraft systems (UAS) and their critical components. This regulatory change prevents new drone models from receiving the equipment authorizations required for legal import and sale in the United States, although it does not impact drones already in use or previously authorized models. The decision follows a national security determination citing risks related to unauthorized surveillance and data exfiltration. Notably, the new restrictions encompass "associated software," directly affecting the digital stack that powers modern AI-assisted navigation and perception in autonomous flight systems.
As drone gifts surge during the holiday season, Australia’s Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA) highlights the importance of operator accountability. While AI-driven features like obstacle avoidance simplify flight, they do not exempt pilots from legal requirements such as maintaining visual line of sight and staying clear of restricted airspace. This report details current safety regulations, enforcement penalties, and the ongoing digital transition toward automated airspace approvals.
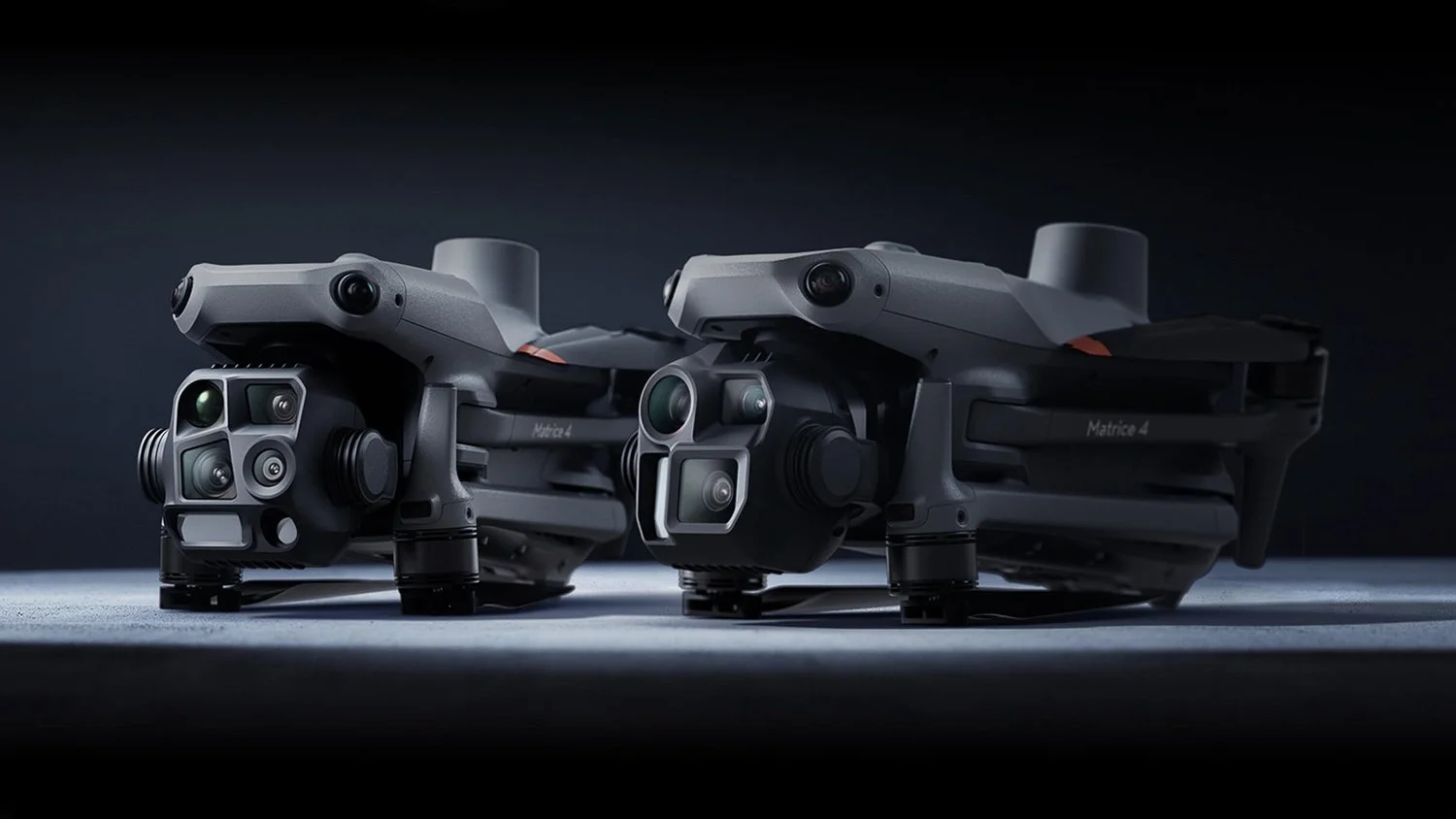
The December 11, 2025, update for the DJI Matrice 4 Series introduces a more flexible AI detection workflow, allowing operators to configure alerts using text descriptions and reference images. Key enhancements to the Patrol Route system now enable automated responses, such as triggering the AS1 speaker or AL1 spotlight upon object recognition, while expanding support for advanced infrared analytics.
Australian drone services provider AUAV has integrated Above Surveying’s SolarGain platform to process inspection data for utility-scale solar farms. The workflow utilizes artificial intelligence to classify thermal anomalies and map them to a site’s digital twin, aiming to improve maintenance efficiency. The report also outlines how this technology aligns with current construction monitoring practices and the Civil Aviation Safety Authority’s (CASA) regulations for remote drone operations.
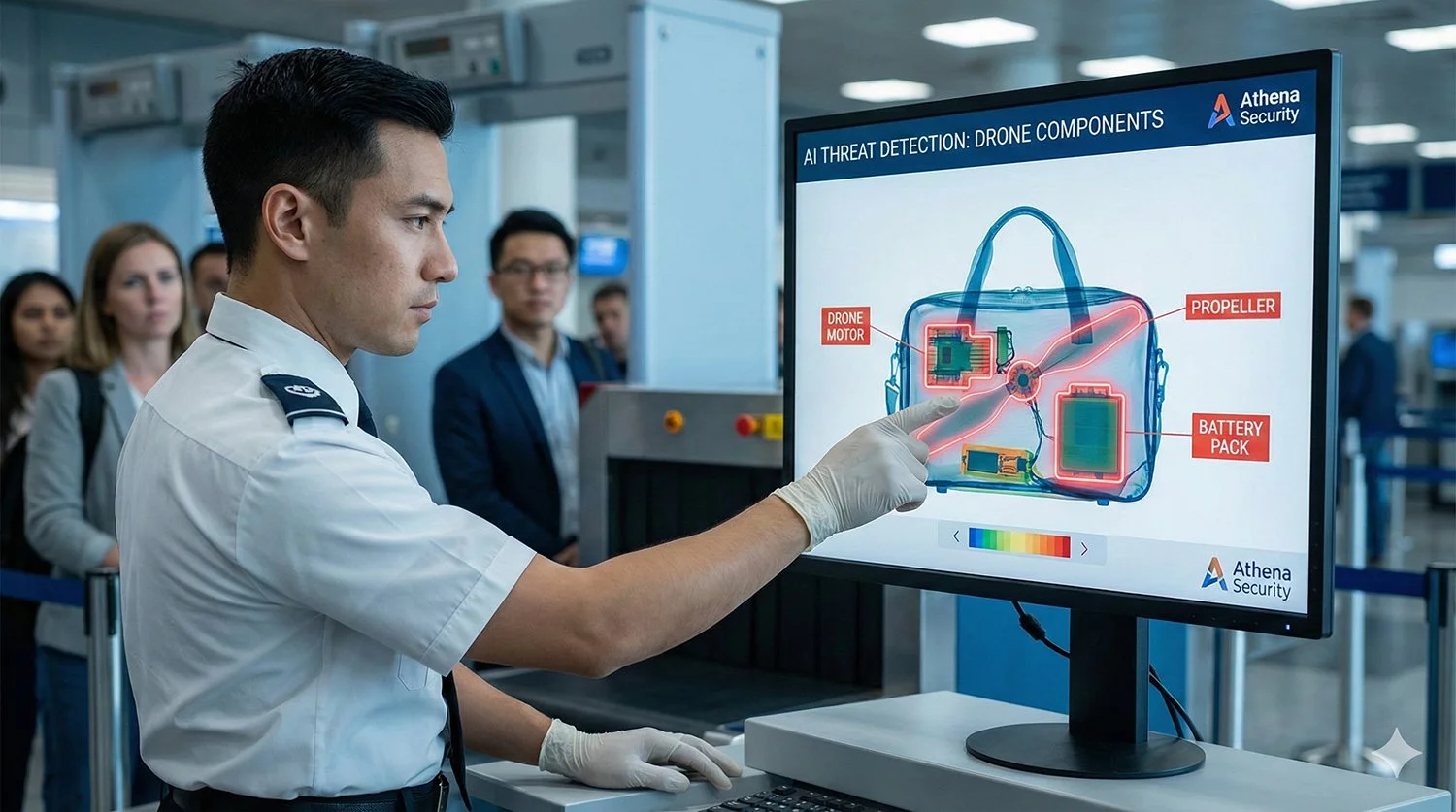
Athena Security has announced a new AI model designed to detect disassembled drone components — such as motors and batteries — within existing X-ray screening workflows. The system targets pre-assembly risks at checkpoints, aiming to mitigate threats before unmanned aircraft can be constructed and launched near critical infrastructure.
On November 25, representatives from more than 50 federal entities—including the FBI, FAA, and military branches—convened to operationalize Joint Interagency Task Force 401 (JIATF 401). Established to address the escalating risks from autonomous and AI-enabled small drones, the task force is charged with synchronizing government efforts and speeding up the procurement of interoperable defensive systems for both homeland security and overseas operations.
As commercial drone flights increase, Unmanned Traffic Management (UTM) systems are adopting artificial intelligence to coordinate low-altitude airspace. This report details recent regulatory shifts, including the FAA’s Part 108 proposal, and reviews real-world trials in Europe aimed at reducing collision risks.
Facing record-breaking barrages of Russian loitering munitions, Ukraine has accelerated the production of low-cost, AI-assisted interceptor drones. Systems such as STING and Octopus are now being fielded to protect airspace and conserve high-value missiles, addressing the critical cost imbalance of modern air defense.
Quantum-Systems, a German drone maker founded in 2015, has grown from agricultural and mapping missions to supplying AI-enabled ISR systems for European and Ukrainian defence forces. With valuation discussions nearing €3 billion, the company reflects Europe’s accelerating investment in dual-use autonomous drones.
Shield AI has revealed the X-BAT, an AI-driven VTOL fighter jet capable of operating without runways. Valued at $5.3 billion and backed by major investors, the company plans first flight trials in 2026 as part of efforts to expand autonomous combat operations in high-risk environments.
DJI’s Mini 5 Pro has entered a regulatory grey zone as many production units weigh slightly above the 250g threshold that exempts hobby drones from stricter requirements. While the EU continues to allow the model under its C0 class through a manufacturing tolerance rule, authorities in the US, UK and Canada apply the limit strictly, meaning some pilots must now register the drone and follow additional operational rules. The situation highlights ongoing challenges in aligning drone standards across regions.
China has introduced a new autonomous military vehicle known as the P60, developed by defence manufacturer Norinco and powered by the homegrown DeepSeek AI system. Capable of supporting reconnaissance and combat logistics with minimal human oversight, the P60 reflects a wider strategy to advance AI-enabled military operations and reduce dependence on foreign technology.
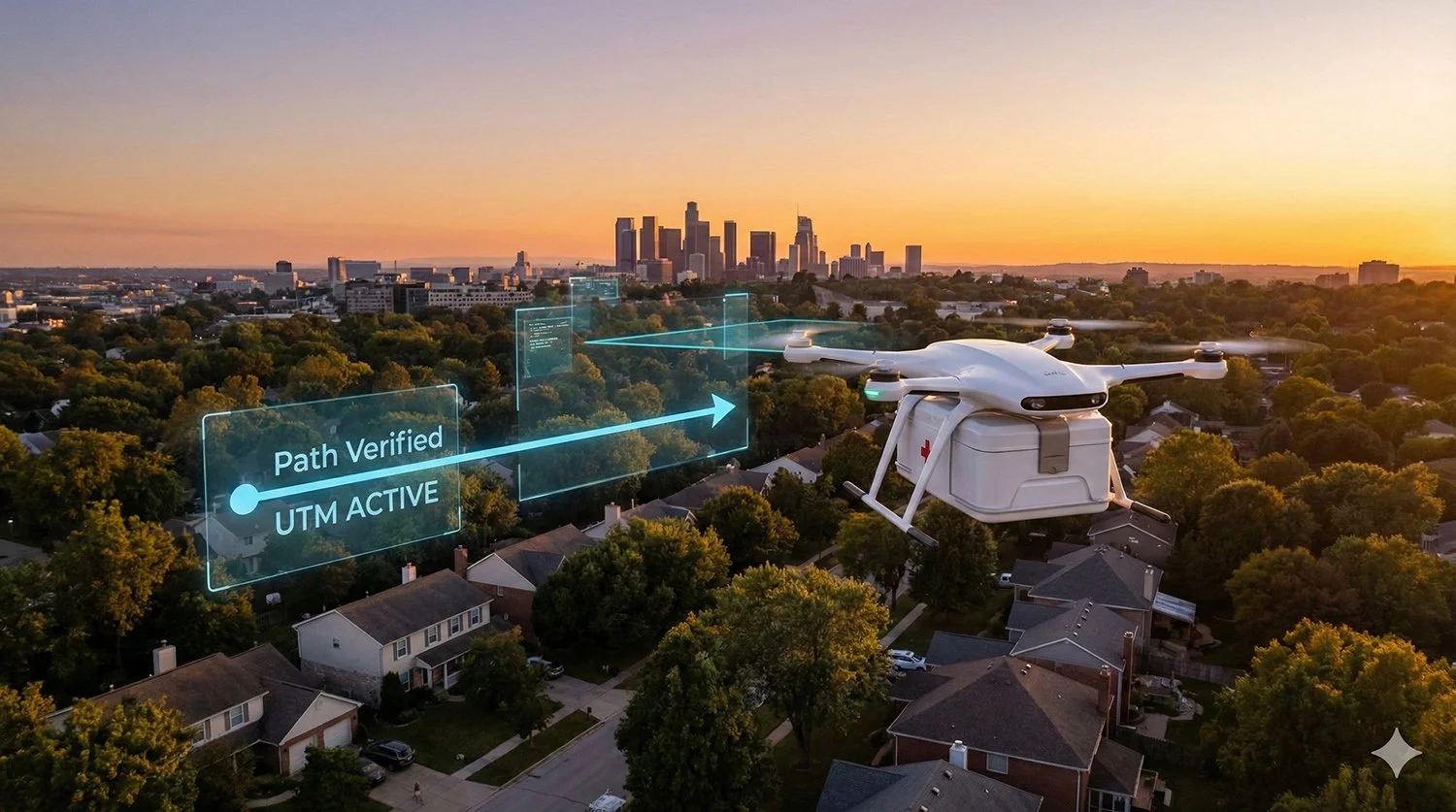
Amazon has launched its latest drone delivery initiative using the MK30 model and advanced artificial-intelligence systems to deliver eligible items weighing up to five pounds within 60 minutes or less in select U.S. regions. The service builds on regulatory clearances, digital mapping and perception technologies, as Amazon advances its use of autonomous logistics in urban settings.
A research team from TU Delft and CWI has shown a quadrotor drone flying stably without an inertial measurement unit, relying instead on visual data from a downward-facing event camera. A compact neural network processes event streams in real time to estimate orientation and rotation rates, marking a step toward lightweight, AI-driven drone navigation inspired by insect flight.
DroneShield has expanded its counter-drone portfolio with SentryCiv, a subscription-based system bringing AI-powered detection to civilian airspace security. Using passive RF sensors and the company’s RFAI engine, SentryCiv offers real-time monitoring, threat prioritization, and quarterly AI updates—making advanced drone detection more accessible to airports, utilities, prisons, and other high-risk sites.
Dropla Tech ApS, founded in 2023 in Denmark with Ukrainian partners, is developing Blue Eyes, an AI platform that enables drones to detect landmines and unexploded ordnance in real time without GPS or cloud reliance. Backed by €2.4 million in pre-seed funding, the company seeks to cut demining costs and timelines, supporting Ukraine’s recovery and advancing global explosive threat detection.
Hong Kong and Brazil are reshaping drone regulations to support AI-driven applications across sectors. Hong Kong’s amendments create a new category for heavier drones and enable sandbox trials, while Brazil’s proposed RBAC-100 framework adopts risk-based oversight to expand agricultural and commercial drone use.
Japan’s Maritime Self-Defense Force has selected Shield AI’s V-BAT drone as its first ship-based ISR platform. The AI-powered system supports autonomous operations in GPS-denied environments and is part of Japan’s broader effort to modernize its defense capabilities in response to regional challenges.
During Drone Show Korea 2025, Bo-Hyung Lee, former commander of South Korea’s Drone Operations Command, emphasized the growing role of artificial intelligence in civilian drone applications. The event showcased AI innovations supporting agriculture, infrastructure, and disaster management, as South Korea advances its position in the global autonomous technology landscape.
On June 6, 2025, President Donald Trump signed two executive orders—“Unleashing American Drone Dominance” and “Restoring American Airspace Sovereignty”—aimed at advancing drone technology across the United States. The initiatives focus on AI-powered regulatory reform, expanded Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) operations, and enhanced airspace security, with significant implications for public safety and domestic innovation.
Ukraine’s push to integrate artificial intelligence into combat drones has drawn global attention. While AI offers potential to counter jamming and reduce operator risk, real-world limitations in terrain, cost, and reliability persist. With Russia advancing its own AI-guided systems, the battlefield has become a proving ground for the future of autonomous warfare.
Hong Kong will host AI+ Power 2025 on June 5-6, spotlighting advances in artificial intelligence and drone technology. The exhibition will present practical AI applications in culture and urban development, reflecting the city’s push toward global tech leadership.
The MQ-28 Ghost Bat, Australia’s first domestically developed combat aircraft in over five decades, showcases the nation’s advances in AI-driven unmanned aviation. Developed by Boeing and the Royal Australian Air Force, the Ghost Bat is designed to work alongside manned aircraft, offering new capabilities in autonomous military operations.
BigBear.ai and Hardy Dynamics have joined the U.S. Army’s Project Linchpin to develop AI-powered drone swarm systems for military use. The project will focus on secure coordination for unmanned aerial systems and is set for field testing at Exercise Talisman Sabre 2025 in Australia, involving AUKUS and allied forces.
UK Defence Secretary John Healey has announced that the upcoming Strategic Defence Review will place a central focus on integrating artificial intelligence and emerging technologies into the armed forces. The review, led by Lord Robertson and Fiona Hill, aims to strengthen the UK’s position in NATO through targeted investments and procurement reforms.
DoorDash and Wing have introduced an AI-driven drone delivery service in Charlotte, North Carolina, offering fast food deliveries from local restaurants to select neighborhoods. The initiative aims to increase convenience, reduce emissions, and test the potential for broader adoption of autonomous delivery technology in the U.S.
License This Article
We are a leading AI-focused digital news platform, combining AI-generated reporting with human editorial oversight. By aggregating and synthesizing the latest developments in AI — spanning innovation, technology, ethics, policy and business — we deliver timely, accurate and thought-provoking content.